In the past, there has been a lot of organic waste from the Cacao harvest. Research has been focused on alternative uses for all the discarded pods and fruit pulp produced during the Cacao bean harvest.
Non-chocolate uses of Theobroma Cacao
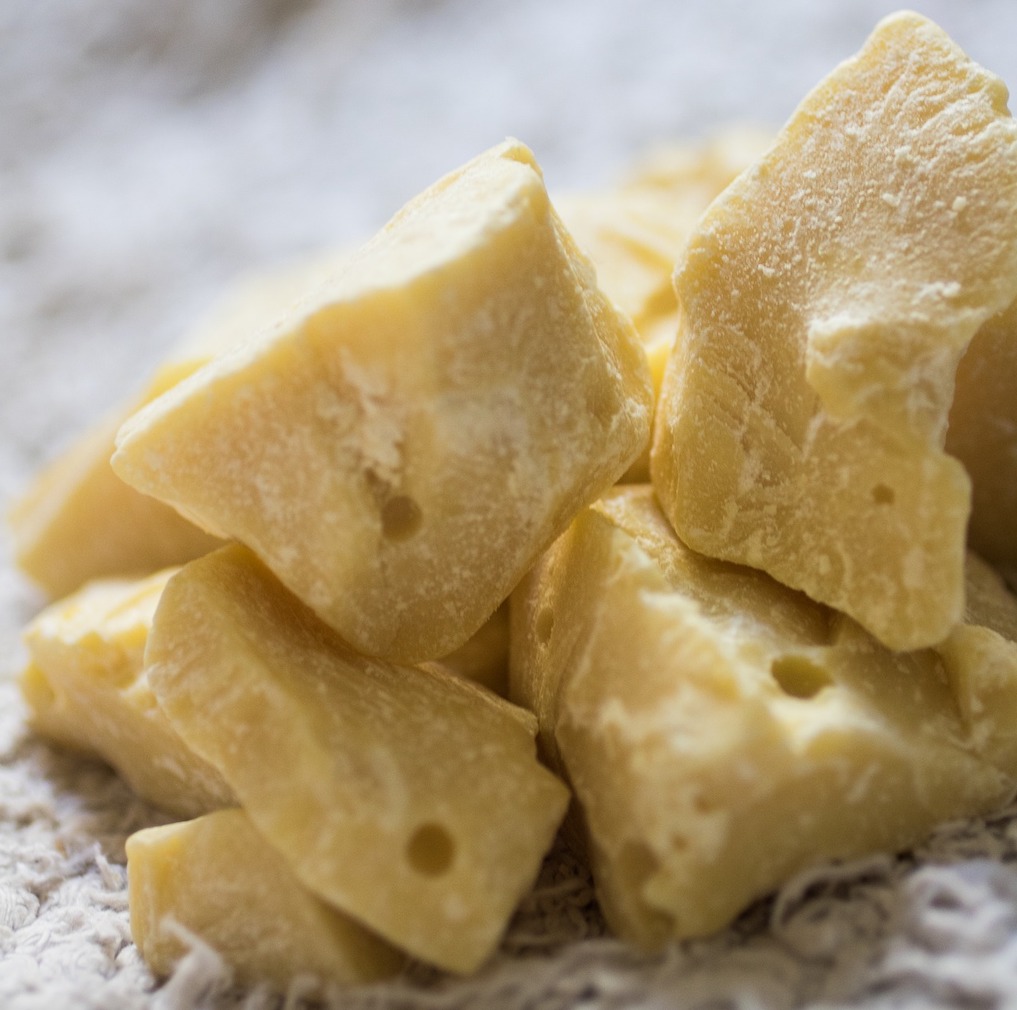
Economically, the most important use of Cacao is for making chocolate and cocoa for all our favourite sweet stuff. Cacao fat, pressed from roasted Cacao beans, is a by-product that has its own uses.
Cacao Butter for Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical uses
The cosmetic industry uses Cacao butter as a nutritionally rich, moisturizing, and emollient fat in numerous skin-care products.
Cacao butter is solid at room temperature but melts at body temperature. Suppositories, meant to dissolve inside the body, are often made with Cacao butter. Lotions for haemorrhoids, vaginal and uterine lesions, or dry, chapped skin, lip balm and wound dressings also frequently contain Cacao butter.
Internally, Cacao butter can help soothe bronchial and intestinal irritations. In fact, even high quality, high percentage Cocoa and Chocolate has some amazing superfood properties.
New uses from waste products
During processing, the beans and some fruit pulp are left to ‘sweat’ for a few days, which changes the beans’ chemistry, reducing their bitterness and creating the right conditions for their characteristic chocolate flavour to develop. Although the pulp is an essential part of this process, only small amounts are. About 60% of the pulp goes to waste.
Cacao smoothies and juices
But it doesn’t have to. In Brazil, farmers remove much of the pulp to modify the acidity and obtain smoother-tasting beans. The fruit pulp is sold at the local market and turned into various delicious products. Cocoa fruit-pulp jelly is a local delicacy. It serves as an ingredient in juices or shakes. But it could also be frozen and used to flavour ice cream, yoghurt or sold as a fruit juice concentrate. Unfortunately, so far, preserving large amounts of pulp has proved difficult and costly.
To find ways to make more of the harvest, besides the beans, would be highly desirable, since Cacao prices on the global market are fickle, putting the small subsistence farmers at risk.
New uses for discarded pods
Traditionally, a certain proportion of discarded pods is fed to animals, but the pods are not very digestible. In West Africa, the discarded pods are burnt to yield potassium-rich ash, used for making soap. But composting them, or making bio-char which in turn could be used to return valuable nutrients to the soil, would reduce farmers’ dependence on chemical fertilizers and reduce their costs. (1)
In recent years, research has focused on other alternative products that could be obtained from Cacao without decreasing pod yields. (Antonio Figueira, Jules Janick, and James N. BeMiller, 1993)
Gum
One such product is gum, present in both the stem and, to a larger extent, in the pods. This gum has a similar composition as Karaya Gum, which is typically extracted from various Sterculia species.
The food- and pharmaceutical industries use it as an emulsifying agent and fixative. Studies show that Cacao pod gum compares favourably with Gum Karaya. Both contain the same monosaccharides, but Cacao pod gum also contains arabinose and has a higher proportion of rhamnose, making it better suited as a binder for pharmaceutical pills. In this respect, it is even superior to Gum Tragacanth. (Figueira et al. 1992).
Due to supply inconsistencies, the demand for Karaya gum has diminished. But Cacao pod gum could provide a superior and readily available alternative that could also provide a secondary source of income for subsistence farmers.
References
(1) Using Cocoa Pod Husks to Improve Crop Yields and Soil Quality
Figueira, A., J. Janick, and J.N. BeMiller. 1993. New products from Theobroma cacao: Seed pulp and pod gum. p. 475-478. In: J. Janick and J.E. Simon (eds.), New crops. Wiley, New York.
Figueira, A., J. Janick, M. Yadav, and J.N. BeMiller. 1992. Cacao gum: a potential new economic product. In: Proc. Int. Cocoa Conf. Challenges in the 90s (in press).
Unten, S., H. Ushijima, H. Shimizu, H. Tsuchie, T. Kitamura, N. Moritome, and H. Sakagami. 1991. Effect of cacao husk extract on human immunodeficiency virus infection. Letters Appl. Microbiol. 14:251-254.