Nature Notes:
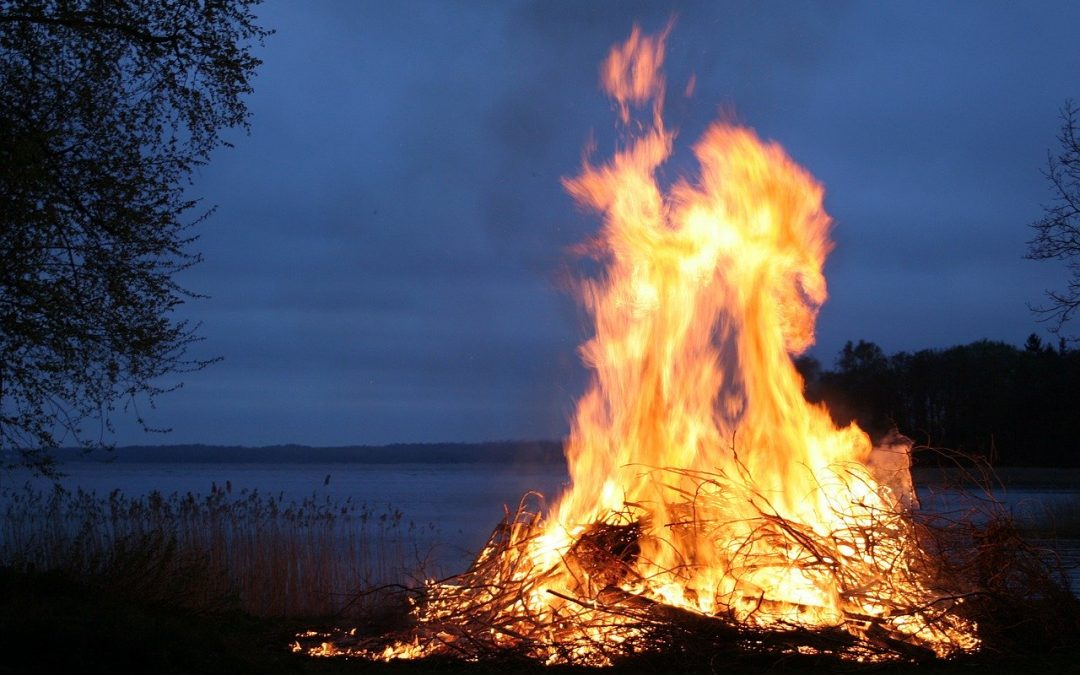

Summer Solstice
Happy Summer Solstice!
At Summer Solstice, the Sun reaches the zenith of its annual journey. We celebrate the longest day and shortest night. It is a magical time: nature is vibrant and the veil between the worlds is thin: sprites and spirits easily cross between them, and we may even catch a glimpse of the little folk.
The young Sun-God Belenos and the Earth Goddess, known by many names, are at the peak of their ecstatic embrace, and all nature takes part in their rapturous exuberance.
At the Summer Solstice, we honour the Gods and celebrate the life force in its generous abundance. Corresponding to the Winter Solstice and the 12 days of Christmas, the Summer Solstice is also celebrated for 12 days. This is a twilight zone, where magic happens. At this time of the year, the gods walk among us and hear our prayers. We ask for protection, health, and sustenance, and pray that they protect our crops from summer storms and fires. We bless the grain and the crops, the barn and the animals.
At the Summer Solstice, the herbs are at their most potent. It is time to gather our annual supplies of St. John’s Wort, Mugwort, Verbena, Chamomile, Mullein, Grund-Ivy (Glechoma hederacea), and more.
Spiritually, the summer solstice marks a threshold. It is a time to seek guidance and answers by divination or to retreat on a vision quest to hold counsel with the gods. At this halfway point in the annual cycle of the year, we reflect on the first 6 months. Have the seeds we planted in the spring sprouted? Are they blossoming and promising to bear fruit? Did we follow our visions and achieve the goals we set at the beginning of the year? Are we on track, or did we wander off into the tall grass along the way?
Are those goals still relevant? Take a moment to reflect, re-align and connect with your inner vision and guiding voice of the higher self. If you have veered off the path, this is an opportunity to adjust course, so you can sail successfully through the second half of the year.
If you are unsure of your direction, this is a perfect time to seek divine guidance by vision quest, pilgrimage, or retreat – whichever way allows you to commune with the gods and silence the noise enough so you can hear the whispers of intuition.
Above all, Midsummer is a time to gather and celebrate, to revel around bonfires, dancing, feasting, and merry-making. The twelve days of the Summer Solstice offer a break from usual activities and encourage us to soak up that pure life force in all its glory.
And yet, this year my heart is heavy, even as I celebrate the eternal powers of the life-force and its abundance. As I write these words, nature is in great peril and distress. Temperatures have risen to levels we normally see in August, and drought wilts the verdant mantle of the earth. War is raging, and worse is looming. Sorrow clouds my joy. I retreat into silence to seek solace and guidance, and to pray for peace.
Happy Summer Solstice, everyone – may peace return to all!
Current issue
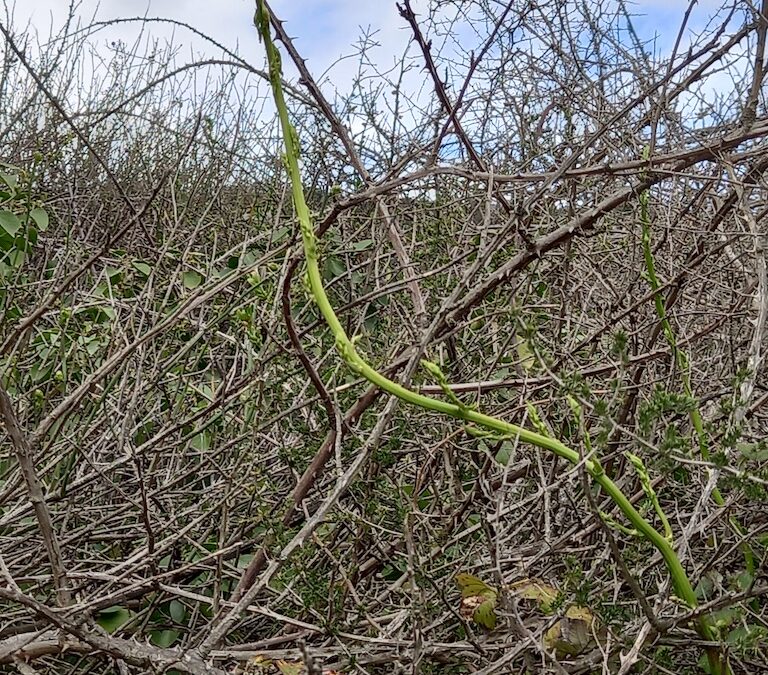

Foraging Wild Asparagus
Foraging Wild Asparagus – A Forager’s Treasure Hunt
Spring is underway, bringing with it its characteristic mixed-bag weather patterns. In some regions, winter stubbornly clings; in others, it’s long forgotten. Where I am, it has not quite sprung, but regardless, there are signs of its imminent arrival. Wild asparagus is sending up its tender shoots, and they are ready for the picking.
While cultivated asparagus typically debuts in May, the wild variety emerges earlier, rewarding keen-eyed foragers with its tender, flavourful spears. Unlike other foraging activities, hunting for wild asparagus is an experience akin to mushroom picking. It requires patience, a trained eye, and a knack for spotting the elusive spears hidden among the prickly thickets of its parent plant and dense undergrowth. Many aspiring foragers walk right past them, oblivious to their presence, until the shoots bolt and become too woody to enjoy as food. But once you develop a sense of the season and get to know their elusive hiding spots, foraging for wild asparagus becomes a thrilling treasure hunt that can lead you to unexpected places.
Where to Find Wild Asparagus
Wild asparagus thrives in a variety of habitats, depending on the species. It favours well-drained soil and typically grows in ditches, riverbanks, and alluvial plains where moisture is abundant but not stagnant. Most species prefer full sun, but some can tolerate semi-shaded areas and heavier soils.
Although its appearance is distinctive, wild asparagus can be tricky to spot. Foraging legend Euell Gibbons, in his classic book Stalking the Wild Asparagus, offers a useful tip: look for last season’s dead asparagus brush, which often serves as a clue to the presence of fresh spears. This method works well for the tall, upright-growing variety, which is often an “escaped” garden asparagus. But, true wild asparagus, Asparagus acutifolius, a native of the Mediterranean Basin, presents a greater challenge. It has a scrambling growth habit, weaving through undergrowth or along the ground. It takes a trained eye to spot the sneaky, snaky spears as they pop through the thicket of older plants.

The History of Wild Asparagus
Wild asparagus is most commonly found in southern Europe, particularly in Spain, Italy, and France. Escaped cultivated asparagus is also found in northern regions, particularly near historical centres of their cultivation. Birds play a key role in dispersing their seeds, aiding their spread far beyond their original habitat.
Asparagus has an ancient history, with records indicating its use in Egypt, Greece, and Rome. The Romans likely introduced it to Northern Europe, where it became a sought-after delicacy thought fit for kings but not peasants. Old herbals praise asparagus not only as a culinary delight, but also as a medicinal plant, valued for its diuretic and cleansing properties.
Nutritional and Medicinal Benefits
Though wild asparagus is no longer widely used medicinally, its health benefits are worth mentioning. Asparagus, wild or cultivated, is a potent diuretic. It stimulates the kidney and liver function while helping to eliminate toxins. Just what the doctor calls for as a spring tonic. It is also rich in vitamins, antioxidants, and fibre, but if too much is consumed, it can rob the body of calcium. (Not a worry for wild asparagus – it is unlikely we will ever find enough of it to cause any such deficits in the body.)
Traditionally, asparagus has been associated with aphrodisiac qualities—a claim that may be linked as much to its suggestive appearance as to any actual physiological effects. But the only way to know for sure is to put it to the test!
 How to Prepare Wild Asparagus
How to Prepare Wild Asparagus
Wild asparagus, particularly the escaped variety, is more slender, tender, and subtly flavoured than its cultivated counterpart. Because of its delicate nature, it requires minimal cooking. Simply trim off the woody ends and lightly sauté the spears or throw them into the pot for the last couple of minutes. They make a delicious addition to omelettes, pasta dishes, and risotto. For a simple, yet divine ‘bonne bouche’, try drizzling them with lemon juice and garlic butter.
Final Thoughts
Foraging for wild asparagus is more than just a way to enjoy a seasonal delicacy—it’s an adventure that deepens your connection with nature. Whether you’re an experienced forager or a curious beginner, the thrill of discovering these hidden treasures makes every spring outing an experience to remember. So, the next time you find yourself wandering through the countryside, keep an eye out for the elusive spears—you might just stumble upon one of nature’s greatest spring delights.
Plant Profile:
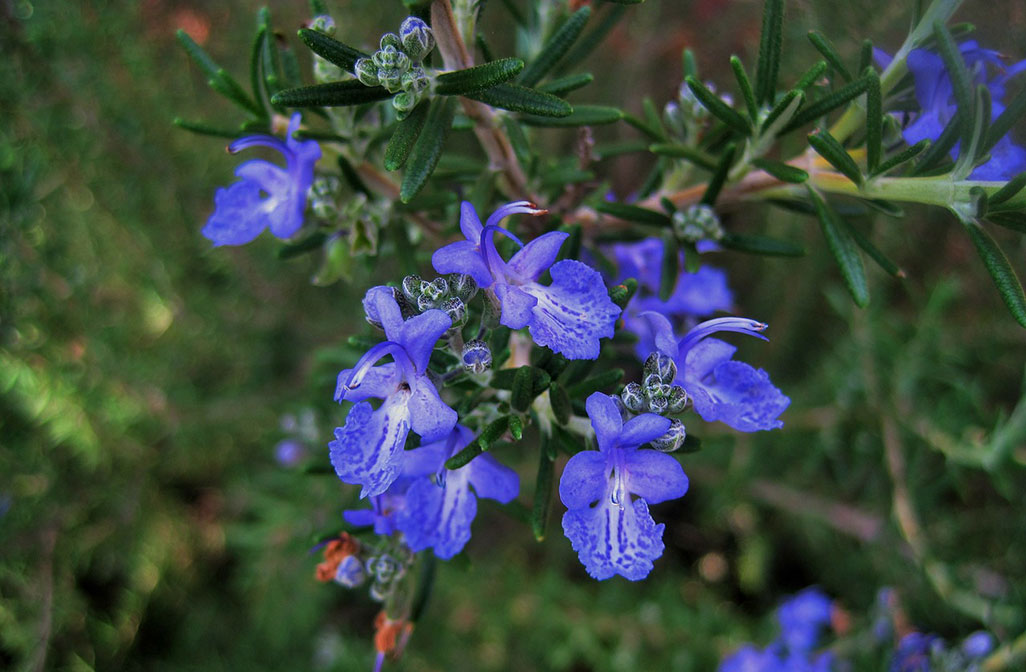

Rosemary – Rosmarinus officinalis
Most of us know this woody, aromatic bush as a culinary herb, but in fact, Rosemary is so much more than that. It has some quite remarkable properties that are well worth remembering.
As a kitchen herb, Rosemary is an old stand-by: Rosemary potatoes, Rosemary chicken, Rosemary salt, Rosemary lamb, or Rosemary fish are all familiar menu items. The needle-like leaves have a highly aromatic, somewhat medicinal scent. The flavour is distinctive, somewhat bitter, and resinous, which perfectly complements fatty foods. It ‘cuts through’ the grease. This is why it is used to flavor greasy meat and fish dishes and to aid digestion. Rosemary acts as a token apology to the liver.
Rosemary, which has long been known as Rosmarinus officinalis, was recently assigned to the Genus ‘Salvia’. That means, it is botanically grouped with the sages. However, the old name is still acceptable, but keep the name change in mind to avoid confusion.
Although it is an herb of the mint family (Lamiaceae), its thin, spiky leaves lend it the appearance of some kind of dwarf conifer. Rosemary is at home in the semi-arid climate zone of the Mediterranean coastal region. It commonly grows in the garrigue, the shrubland that covers the lower hills. Its scientific name – ‘rosmarinus’ means ‘Dew of the Sea’. It indicates that this herb likes to be ‘kissed’ by the salty mist coming in from the sea. Others have suggested that the name perhaps alludes to the light blue flowers. A bush that is profusely covered in flowers has the appearance of sea foam on the crest of a wave. Thus, Rosemary has also been linked to the Greek Goddess Aphrodite, who was born from the foam of the sea.
In the Mediterranean, it is one of the earliest flowers to appear in the New Year. Its pale blue flowers blush the wild coastal hillsides, spreading an aromatic scent that awakens the sleepy bees. Rich in nectar, Rosemary is one of their first sources of nourishment. The highly aromatic Rosemary honey is sold at local markets as a highly prized regional specialty.
Rosemary’s intense fragrance and aromatic flavor are due to essential oils, which are obtained not from the flowers, but from the needle-like leaves. As a key ingredient of the ever-useful herb blend known as ‘Herbes de Provençe’ it is a quintessential item on the herb shelf.
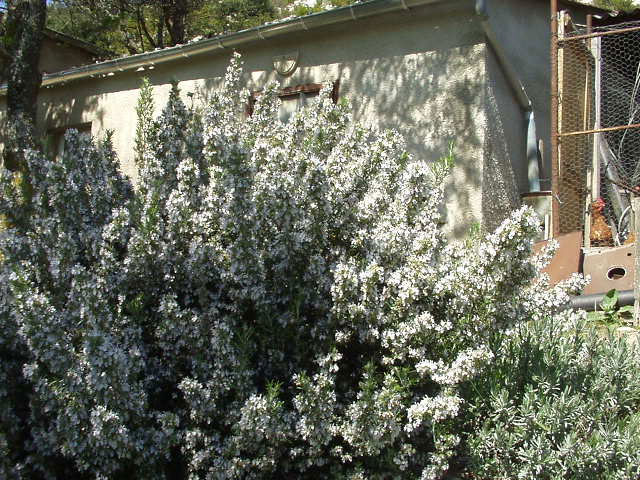

Medicinal uses of Rosemary
This essential oil is also responsible for its medicinal properties. Rosemary oil stimulates blood circulation, particularly to the head. It has a beneficial effect on memory. In herbal lore, this property is associated with the remembrance of loved ones, and friends, and those who have recently passed away.
Rosemary’s bitter principle aids digestion. It ‘warms’ the stomach and stimulates the liver and gallbladder. It helps the body to break down fats and improve digestion.
It also shows anti-viral, anti-bacterial and anti-fungal properties. Externally, a Rosemary infusion can be used to cleanse badly healing wounds.
Cooking with Rosemary
Rosemary goes great with roasts – whether you are roasting a goose, lamb chops, or a pan full of root vegetables, a sprig of rosemary transforms the dish and adds a complex, slightly bitter and highly aromatic flavor.
Purification
Rosemary has also long been used as incense, particularly in combination with Juniper berries. This tradition has continued into modern times. It is still sometimes used to fumigate and purify the air in a patient’s room. It is also popular as a cleansing aromatic that is used in sauna infusions, or to scent bath oils and soaps.
Restorative
Rosemary’ is a tonic and restorative. Its stimulating action on the blood circulation and coronary function and can restore vitality and strength to convalescents or feeble children. In the past it was also used as an aphrodisiac that had the reputation to restore a dwindling manhood. Recent research has shown that Rosemary contains
Cosmetics
Rosemary can be added to home-made shampoos or hair rinses. It will stimulate the follicles and promote hair growth. In the ‘still room,’ its essence would have been added to skin tonics, lotions, and oils.
Rosemary Hair Rinse
The simplest way to let your hair benefit from the tonic power of Rosemary is to simply make a strong infusion of 1 tablespoon of dried rosemary leaves to 500 ml of water – infuse with boiling water and steep until it has cooled down, strain and massage into the scalp. Leave it for a few minutes, then rinse it out. It is best when prepared fresh, but it will keep for a few days in the fridge.
Rosemary Shampoo
Unscented shampoo bases are readily available at many stores these days. Get one you like and add a few drops of Rosemary Essential Oil to it.
Recommended for brown or dark hair as it will naturally darken the hair over time.
More articles:
Rosemary – Rosmarinus officinalis
Most of us know this woody, aromatic bush as a culinary herb, but in fact, Rosemary is so much more than that. It has some quite remarkable properties that are well worth remembering. As a kitchen herb, Rosemary is an old stand-by: Rosemary potatoes, Rosemary chicken,...
Foraging Chickweed
Chickweed is a little sprawling herb with heart-shaped leaves and star-shaped flowers that belongs to the Pink family. Gardeners hate it.
Making Birdseed Feeders
During the winter, birds don’t always find enough food. Learn how to make simple birdseed feeders with very few materials, in next to no time
Preserving the Harvest (1)
This article is about various methods to preserve the harvest. Making your own pickles and preserves, jams and chutneys, liqueurs and canned veggies is a great way to celebrate the harvest
Plant Profile: St. John’s Wort
This plant profile of St. John’s Wort tells the stories, traditions, and medicinal uses of St John’s Wort.
Gardening Jobs in July
This is the time of the year that every gardener is waiting for! The garden is in its prime. Everything is grown, flowering and fruiting, and it is a sheer joy to be out there enjoying nature’s bounty.
Gardening Jobs in May
What gardening jobs are there to do in May? Actually, there are plenty. May is one of the busiest gardening months. Sowing, planting, weeding, maintenance and more – there is plenty to do.
Gardening Jobs for March
What gardening jobs are there to do in March? This is a quick guide to what to do and sow in the garden in March.
Gardening Jobs in February
Even as early as February, there are things you can do to kick off the gardening season and get a nice head start.
What is Foraging?
What is foraging, why do people forage, what are wild edible plants and what skills do foragers need to learn?
Slugs
Slugs may not be pretty or cute, but they do play their part in nature, and they are a lot more interesting than I ever thought!
Star of Bethlehem
The Star of Bethlehem is a small bulbous flower of the Lily family with many unusual features and interesting properties.