Nature Notes:

Lughnasad – Harvest Time
The time of the grain harvest
Lughnasad marks the harvest season. Fruits and vegetables ripen, the grain has turned golden, and the grapes grow plump and sweet. It is an intensely busy and happy time, especially for gardeners. We toiled in the spring, and now it is time to harvest the fruit of our labour and enjoy them.
The period from spring to late summer is fraught with danger. Late frosts can kill sensitive starts, and summer storms may ruin a crop in just a few minutes. A good harvest is always hoped for, but never guaranteed. This year, we are witnessing the devastating effects of climate change. After many years of exceedingly hot and dry springs and summers, this year we had unseasonably wet weather. Without water, there is no life. But too much water is no good either. It washes away the topsoil and drowns plants and animals.
In the Christian tradition, Lammas marks the harvest season. The name comes from the Anglo-Saxon word ‘hlaf-mas’, meaning ‘loaf mass’. Bread and wine are the traditional sacraments of the Eucharist. And this is the period, when corn and grapes are getting ready to harvest.
But harvesting the seeds is only one stage of the perpetual cycle of life. Ideally, what we harvest now should sustain and nourish us through the winter, when the Earth is barren and still. To sustain life, a part of the harvest is sacrificed and returned to the earth. We reap as we sow, but we also sow what we reap.
Facing the unravelling climate catastrophe, we are grateful for anything we can harvest today. We must change our practices and learn to adapt and live more sustainably. We depend on Mother Earth and if we want this cycle to continue and provide for our children and children’s children, we must act now.
There are many solutions, but continuing in the old ways is not among them.
The future starts now.
Current issue

Making Birdseed Feeders
How to make Birdseed Feeders
During the winter, birds don’t always find enough food. To help them through these times of scarcity, why not offer them some ‘birdseed feeders’. They are really easy to make and much appreciated. All you need is birdseed (you can use pre-packed supplies, or mix your own, using a blend of edible seeds, nuts, and dried fruit, such as sunflower seeds, buckwheat, oats, millet, linseed, wheat, cracked peanuts or hazelnuts, raisins, etc, some hardened vegetable fat, suet or tallow.
Birdseed Cookies
To make ‘Birdseed cookies’ you can use Christmas cookie cutters.
Materials:
- 250g of hardened coconut fat
- 500g of birdseed mix
- string
Method:
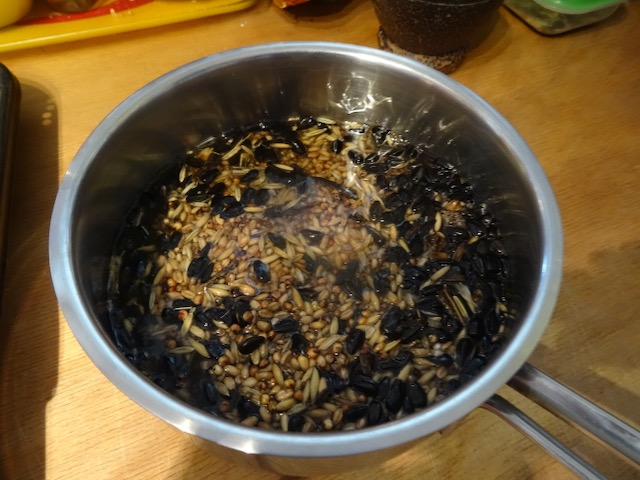
- Melt the fat in a saucepan
- pour in the seed mixture until the fat is almost completely saturated
- Stir well.
- Allow the mixture to cool until it hardens to the consistency of peanut butter.
- Line a baking tray with baking paper and arrange your cookie cutters or shapes
- Now you can spread the seed mixture into the cookie cutter with a spoon or spatula
- Use a toothpick to poke a hole through which you can thread the string once the cookie has completely hardened.

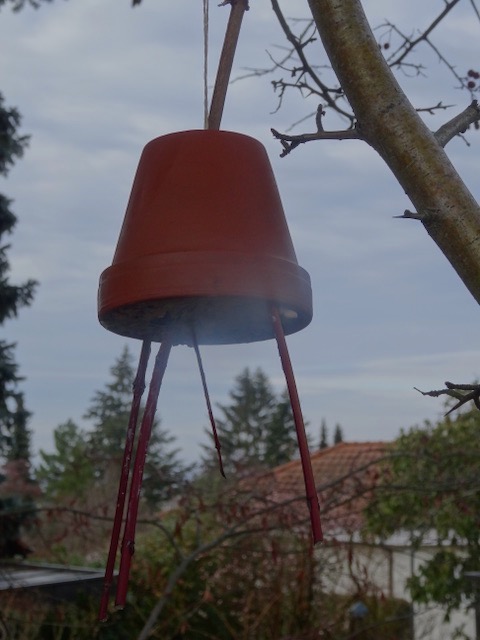
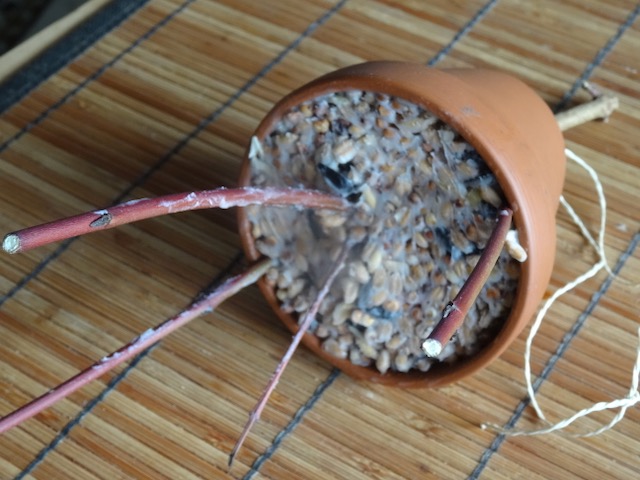
Flowerpot feeders
These are also easy to make. You’ll need small terracotta flowerpots with a hole in the bottom
Materials
- 250g birdseed mixture
- 500g suet or hardened coconut butter
- a swig of sunflower oil
- small flowerpots
- forked twigs
- string
Method
Take a forked twig and pull the straight end through the bottom of the flowerpot.
Fasten with a piece of string and pull the string ends through the hole as a hanger for the flower pot.
I used a second, short twig to fasten it securely. The forked end of the stick should stick out at the open end of the pot.
Make the seed mixture as before, but add a little swig of sunflower oil (not too much!) to keep the seed mixture a little bit softer.
Allow the mixture to cool until it has the consistency of peanut butter.
Fill the pot with the fat/seed paste and allow it to harden some more so that it won’t drip out of the pot.
Now find a tree or better still, a bush that is not accessible to cats (e.g. hawthorn tree or elderflower tree) to hang your ornaments and flowerpot feeders.

Plant Profile:

What is Foraging?
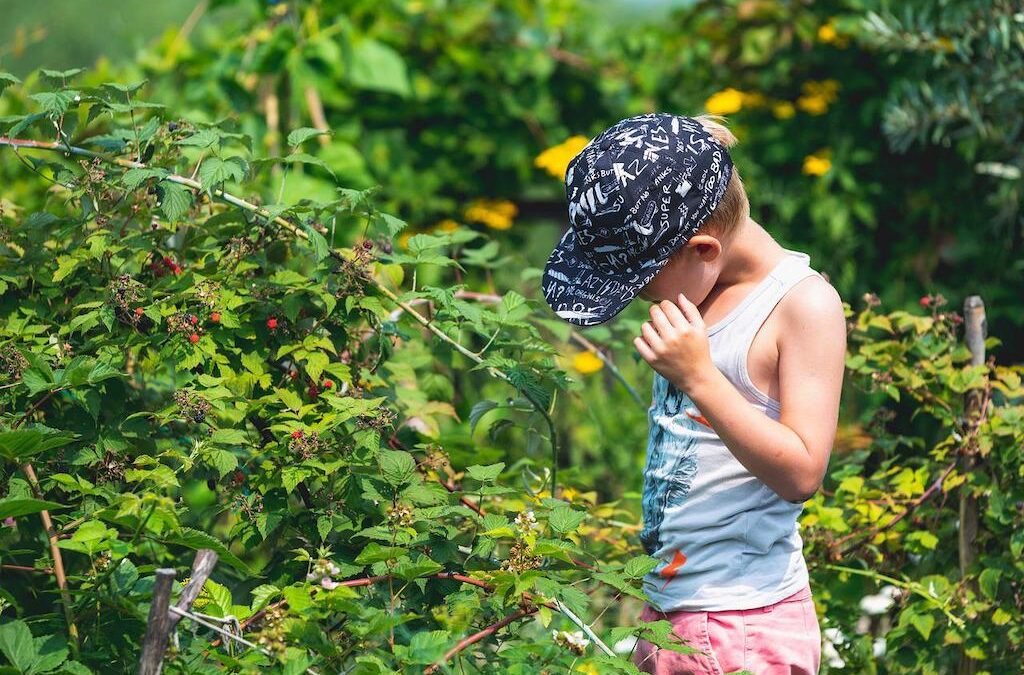
Foraging – connecting with nature through the senses
I became a forager at the age of 5, and I suspect many of you did, too. My early childhood memories are filled with berries of all kinds: wild strawberries, raspberries, blackberries, and above all, blueberries. They covered the forest floor so densely that it was difficult to set down your foot without squashing them.
The summer holidays were pure berry bliss as I munched my way through the landscape like an insatiable caterpillar.
These early sensuous experiences sowed the seeds from which, in time, my passion for nature sprouted.
Nothing can forge a deeper connection to nature and the land than such total immersion – learning by smelling, tasting, eating, feeling and playing with what nature provides in abundance. We learn by doing, observing and asking questions about what we can directly experience. These sensory impressions form the foundations of our understanding of the world.
We learn to understand processes, to see patterns from which we deduce meaning. Such intense observation creates a deep relationship with the observed. We are no longer separated, but deeply and empathically involved. A sense of familiarity and caring develops and gradually grows. A great way to stimulate this learning process is to become a forager.
What is foraging?
The term ‘foraging’ is often associated with animals roaming around looking for food. Different animals forage for different kinds of food. A hedgehog looks for beetles, snails and fallen fruit, while gorillas sustain themselves only on leaves.
As ‘civilized’ human beings, we mostly forage at the supermarket. Everything is always available, and most of us have lost any sense of connection to the cycle of the seasons and the different foods they produce – unless they are gardeners, of course. But before we began domesticating wild species of plants and animals, we incorporated a wide variety of wild species into our diets.
Picking berries or hunting for mushrooms is still hugely popular, especially in times of economic hardship. Some of us continue to forage for part of our diets – not just to save money on the grocery bill, but simply because we love it. We love the connection with the land and the variety of foods and flavours each season provides. Besides, wild foods tend to have a vastly superior nutritional profile compared to industrially farmed produce.
What are wild (plant) foods?
Wild food plants are simply edible plants that are not under cultivation. But the dividing line between wild and cultivated foods can be very vague. Many wild edibles are the undomesticated ancestors of the plants we find at the grocery. Some wild species used to be cultivated and sold on the market but are no longer grown today. Gardeners even curse them as weeds.
Some fruits and nuts are cultivated and found in the wild. The cultivated varieties are bred for specific traits and qualities, such as shelf-life. Their wild cousins tend to be smaller but are often more flavourful.
Whether we can digest any given wild plant is determined by our physiology. Certain plants that would kill us are perfectly edible for other animals.
How to become a forager?
Foraging is a skill that must be learnt like any other.
The best method to learn is to find a knowledgeable mentor or join foraging walks and classes in your neighbourhood.
But there is also much you can learn on your own.
Essential foraging skills:
Learn all you can about your environment
Observe closely, and ask questions:
What kinds of trees, bushes and wildflowers grow here?
Which animals feed on them?
Do certain plants always grow together?
What is the soil like, chalky or loamy, wet or dry?
Do you know what the farmer sprays on his nearby field?
Learn plant identification skills
Foragers must learn basic botany and become familiar with the transformative processes of plants. Learn to recognize them at different stages of their growth cycle. Some species are edible at one stage, but toxic at another.
Learn the seasons
Each season brings forth its special treats, but seasons are not fixed by a calendar. If you know how to read the signs of nature, you will recognize when the time to harvest a specific herb or fruit has come.
Learn how to care for your environment
As foragers, we are stewards of the land, not pillagers. We must not only take but also give back to nature. Remember that you are not the only hungry one out there. Others (human or animal) also depend on the gifts of nature.
Cautions:
Never ever rely on your intuition alone! Even deadly plants and fungi may look, smell or taste deceptively appealing!
Learning everything you can about your environment is the most essential skill a forager must develop.
Always test for allergies before tucking into a foraged feast. The body can be finicky when we ask it to accept foods it has never previously encountered.
And finally – knowing your land also means learning about dangers that may lurk in the undergrowth: snakes, insects (ticks!), wild boars, or even bears, depending on where you live.
Resources:
There are many knowledgeable people out there who teach foraging as a craft – too many to name them all here.
But here are a few useful books. (As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.)
Keep in mind that each bioregion is unique. There are many differences concerning microclimates, seasons, and habitats. Obviously, I can’t cover them all. I focus on my local bioregion, which is Central Europe.
More articles:
Plant Profile: Aloe vera
Plant Profile Aloe vera – Aloe Vera is no longer an exotic stranger. It has found its way into all kinds of common household products from washing-up liquid to latex gloves, and even razors.
Gardening Jobs in June
If you thought that now the growing season is in full swing you can kick back and relax, you are mistaken. June is a rather busy month in the garden, especially if you want to continue harvesting veggies in the fall and winter.
Permaculture – Paradigm Shift for a Sustainable Way of Life
The paradigms of Permaculture, are based on abundance, cooperation, and sharing and seeks to restore rather than exploit ecosystems.
Plantains – Plantago sp.
As masters of adaptation, Plantains are ubiquitous. They have managed to eke out a living in almost every conceivable kind of habitat.
Dyeing Easter Eggs – Naturally
Dyeing Easter Eggs with natural colours is a lovely project to do with kids. Find out how to do it at home.
Natural Dyes – The Colours of Nature
The art of natural dyeing comprises a huge body of knowledge. It is a crafter’s plant knowledge that is passed on by using it.
Foraging Goutweed (Aegopodium podagraria)
Foraging goutweed is one of spring’s delights. It is plentiful, tasty and versatile! It can be used as a pot herb for soups, and fillings, or as pesto.
Sugar Maple – A Sweet Miracle
Sugar Maple is an iconic tree of the northeastern parts of the US. Its display of bright orange and red fall foliage is world-famous.
Happy Valentine’s Day
It’s Valentine’s Day – time to spread some loving. But will you say it with flowers, with chocolate, or a special Valentine’s dinner?
Victorian Flower Language
The Victorian flower language, also known as floriography, was a secret code used to convey your true heart’s desire, without making a sound.
Ways to cope with Stress and Anxiety
We live in stressful times and many of us are feeling anxious. This article outlines ways that can help you to deal with stress and anxiety
Foraging Wintercress – Barbarea vulgaris
Wintercress is winter-hardy and can be foraged during the winter. It is rich in vitamin C and A and used to be known as an ‘anti-scurvy’-herb.