Nature Notes:

Autumn Equinox
Happy Autumn Equinox!
On the Autumn Equinox, night and day are equal. Light and dark are in perfect balance. The Equinox marks the beginning of the end of the harvest season. We celebrate the gifts of the Earth and give thanks. In the Northern Hemisphere, the life-force begins its slow decline as it retreats into the subterranean realm of Hades. The days are getting shorter and cooler; summer is over. We celebrate the joys of the summer and are grateful for the harvest blessings.
The end of the summer is often intensely busy with hunting for nuts and mushrooms, preserving the gifts of the Earth and preparing for the coming dark season.
Stock up the larder and gather the supplies you need to see you through the winter.
Returning to work, we concentrate and focus on our projects and goals. But don’t forget to enjoy the pleasures of this in-between season, as nature explodes its dazzling display of autumn colours.
Image by Sabrina Ripke from Pixabay
Current issue
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
Plant Profile:

Cacao can do more – New Uses for an Old Crop
In the past, there has been a lot of organic waste from the Cacao harvest. Research has been focused on alternative uses for all the discarded pods and fruit pulp produced during the Cacao bean harvest.
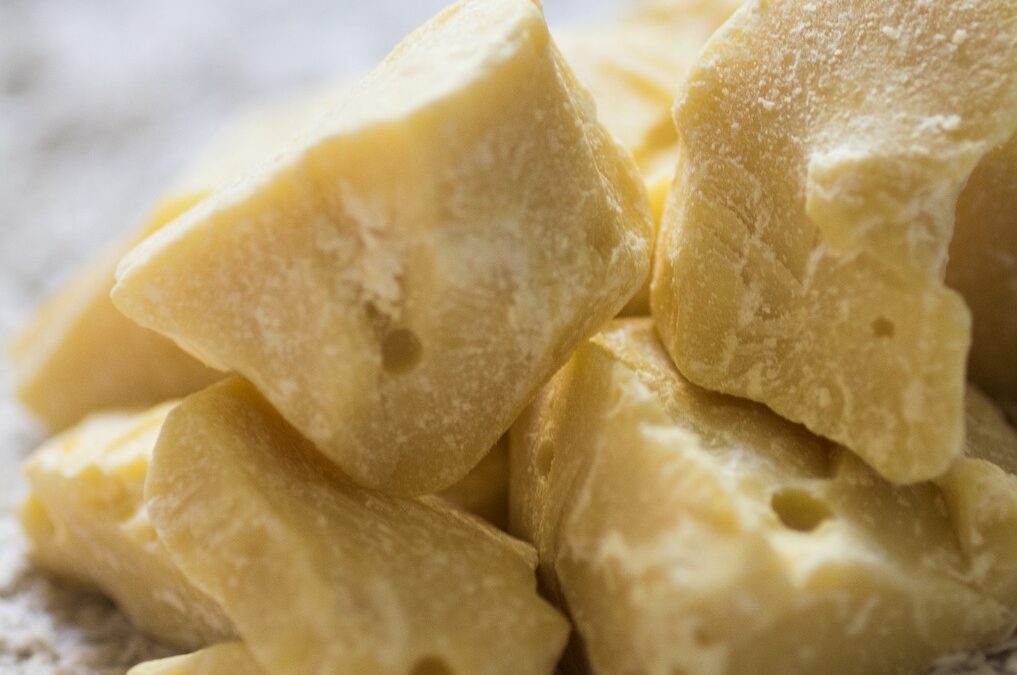
CACAO BUTTER :
A white /yellowish oil, expressed from the crushed seeds
CONSTITUENTS:
Palmitic, Stearic-, Oleic-, Linoleic Acid, traces of Isoleic acid
ACTIONS:
Emollient and nutrient
Non-chocolate uses of Theobroma Cacao
Economically, the most important use of Cacao is for making chocolate and cocoa for all our favourite sweet stuff. Cacao fat, pressed from roasted Cacao beans, is a by-product that has its own uses.
Cacao Butter for Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical uses
The cosmetic industry uses Cacao butter as a nutritionally rich, moisturizing, and emollient fat in numerous skin-care products.
Cacao butter is solid at room temperature but melts at body temperature. Suppositories, meant to dissolve inside the body, are often made with Cacao butter. Lotions for haemorrhoids, vaginal and uterine lesions, or dry, chapped skin, lip balm and wound dressings also frequently contain Cacao butter.
Internally, Cacao butter can help soothe bronchial and intestinal irritations. In fact, even high quality, high percentage Cocoa and Chocolate has some amazing superfood properties.
New uses from waste products
During processing, the beans and some fruit pulp are left to ‘sweat’ for a few days, which changes the beans’ chemistry, reducing their bitterness and creating the right conditions for their characteristic chocolate flavour to develop. Although the pulp is an essential part of this process, only small amounts are. About 60% of the pulp goes to waste.
Cacao smoothies and juices
But it doesn’t have to. In Brazil, farmers remove much of the pulp to modify the acidity and obtain smoother-tasting beans. The fruit pulp is sold at the local market and turned into various delicious products. Cocoa fruit-pulp jelly is a local delicacy. It serves as an ingredient in juices or shakes. But it could also be frozen and used to flavour ice cream, yoghurt or sold as a fruit juice concentrate. Unfortunately, so far, preserving large amounts of pulp has proved difficult and costly.
To find ways to make more of the harvest, besides the beans, would be highly desirable, since Cacao prices on the global market are fickle, putting the small subsistence farmers at risk.
New uses for discarded pods
Traditionally, a certain proportion of discarded pods is fed to animals, but the pods are not very digestible. In West Africa, the discarded pods are burnt to yield potassium-rich ash, used for making soap. But composting them, or making bio-char which in turn could be used to return valuable nutrients to the soil, would reduce farmers’ dependence on chemical fertilizers and reduce their costs. (1)
In recent years, research has focused on other alternative products that could be obtained from Cacao without decreasing pod yields. (Antonio Figueira, Jules Janick, and James N. BeMiller, 1993)
Gum
One such product is gum, present in both the stem and, to a larger extent, in the pods. This gum has a similar composition as Karaya Gum, which is typically extracted from various Sterculia species.
The food- and pharmaceutical industries use it as an emulsifying agent and fixative. Studies show that Cacao pod gum compares favourably with Gum Karaya. Both contain the same monosaccharides, but Cacao pod gum also contains arabinose and has a higher proportion of rhamnose, making it better suited as a binder for pharmaceutical pills. In this respect, it is even superior to Gum Tragacanth. (Figueira et al. 1992).
Due to supply inconsistencies, the demand for Karaya gum has diminished. But Cacao pod gum could provide a superior and readily available alternative that could also provide a secondary source of income for subsistence farmers.
References
(1) Using Cocoa Pod Husks to Improve Crop Yields and Soil Quality
Figueira, A., J. Janick, and J.N. BeMiller. 1993. New products from Theobroma cacao: Seed pulp and pod gum. p. 475-478. In: J. Janick and J.E. Simon (eds.), New crops. Wiley, New York.
Figueira, A., J. Janick, M. Yadav, and J.N. BeMiller. 1992. Cacao gum: a potential new economic product. In: Proc. Int. Cocoa Conf. Challenges in the 90s (in press).
Unten, S., H. Ushijima, H. Shimizu, H. Tsuchie, T. Kitamura, N. Moritome, and H. Sakagami. 1991. Effect of cacao husk extract on human immunodeficiency virus infection. Letters Appl. Microbiol. 14:251-254.
More articles:
Preserving the Harvest (2)
What to do with all the excess fruit? Homemade wines and liqueurs may be just the answer to your bucketloads of fruit
Climate Change – what can we do?
"The climate emergency is THE defining issue of our times." It is the beginning of August, the time of ripening fruits. The year is progressing rapidly and the sun is already past its peak. It has been a stormy first half of the year with weather extremes throughout...
Plant Profile: Corn (Zea Maize)
Plant Profile Corn, (Zea Maize), the ‘staff of life’ of the Americas, its history, mythology and uses, medicinal properties and recipes
Plant Profile: Opium Poppy (Papaver somniferum)
Poppies come in almost every color. The flowers have an ephemeral appearance, quite otherworldly and mysterious.
Let Your Foods Be Medicines
Nutrition plays a vital part in maintaining good health. Common foods have healing properties, yet, are much safer to use than chemically more potent drugs.
Blueberries (Vaccinium myrtillus)
Summer is berry bliss. Bilberries are not just delicious but also incredibly healthy. Medicinal information and recipes.
What are Essential Oils?
What are essential oils? History and uses of essential oils, methods of extraction, various applications, and any potential concerns
Plant Profile: Medicinal Uses of Rose
Roses have long been valued for their various medicinal benefits. The petals are rich in essential oils, while the rosehips are rich in vitamins. The seeds are a valuable source of GLA
Plant Profile: Rose History (1)
Everybody knows and loves the thorny, but beautiful rose, as a universal symbol of love, although we are mostly familiar with the cultivated varieties.
Foraging Wild Strawberries
I adore wild strawberries! As far as I am concerned they are the ULTIMATE wild food.
the Elder-tree in myths, magic, and medicine
The Elder tree is the medicine cabinet of the country people. This much loved, bushy tree is a common sight throughout Britain, Europe, and North America.
The Old Tree and the Carpenter
A parable about the ‘usefulness’ of other species’, vs. the innate value of all species for their own sake, and the preciousness of life.